When embarking on a mobile app development project, having a comprehensive contract isn’t just recommended—it’s essential for protecting your business interests and ensuring project success. Whether you’re a startup founder bringing your first app idea to life or an established business expanding into mobile, the contract you sign with your development team will serve as the foundation for your entire partnership.
A well-crafted app development contract does more than outline basic project details. It establishes clear boundaries, defines ownership rights, ensures legal compliance, and provides a roadmap for resolving potential conflicts. Without these critical elements, you risk facing costly disputes, losing control of your intellectual property, and encountering legal complications that could derail your entire project.

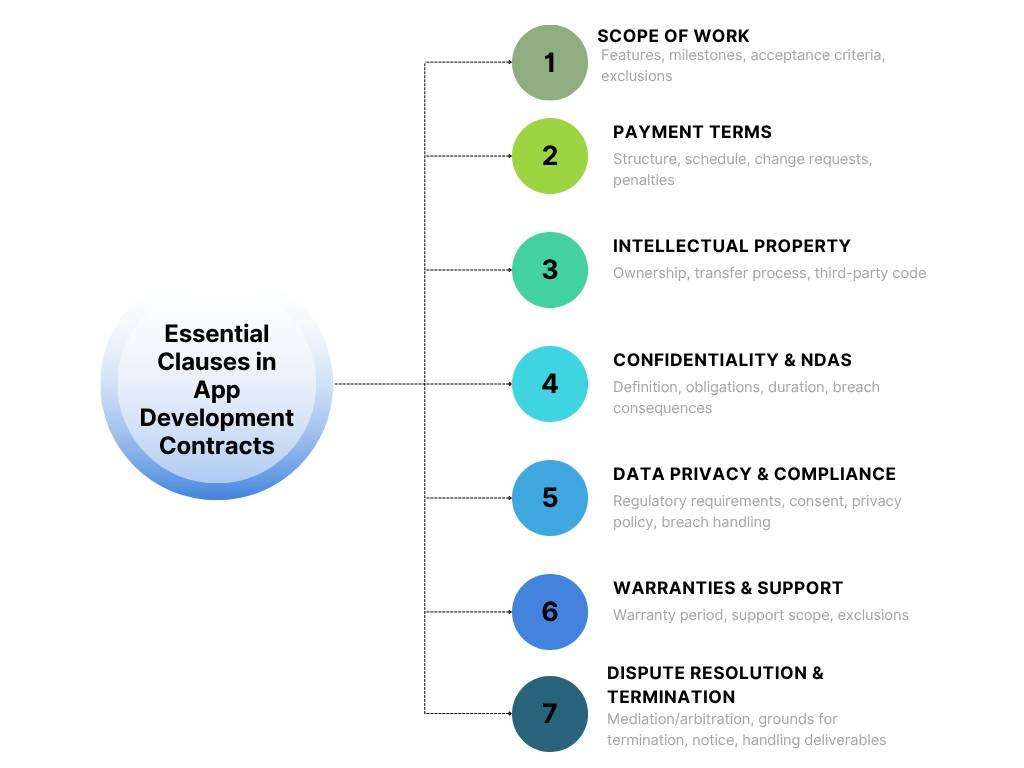
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the seven essential clauses that every app development contract must include to safeguard your interests and set your project up for success.

1. Scope of Work
Why It Matters:
The scope of work serves as the project’s blueprint, defining exactly what your development team will deliver and when. Without this crucial foundation, misunderstandings about deliverables become almost inevitable, leading to scope creep, budget overruns, and timeline delays.
What to Include:
1.1 Detailed App Specifications
Your contract should include a comprehensive description of your app’s features, functionalities, and target platforms. This means specifying whether you’re developing for iOS, Android, web, or multiple platforms, along with detailed feature lists and user experience requirements.
1.2 Project Milestones and Timelines
Establish clear project phases with specific deadlines and deliverables. This might include wireframe completion, UI/UX design approval, beta testing phases, and final launch preparations.
1.3 Clear Exclusions
Just as important as defining what’s included is clearly stating what’s not. This prevents developers from being held responsible for features or services that weren’t part of the original agreement.
1.4 Acceptance Criteria
Define the specific conditions that must be met for each deliverable to be considered complete and acceptable. This removes ambiguity and ensures both parties understand when work meets the required standards.
A clearly defined scope reduces the risk of “scope creep”—the gradual expansion of project requirements that can derail timelines and budgets—and ensures both parties remain aligned throughout the development process.
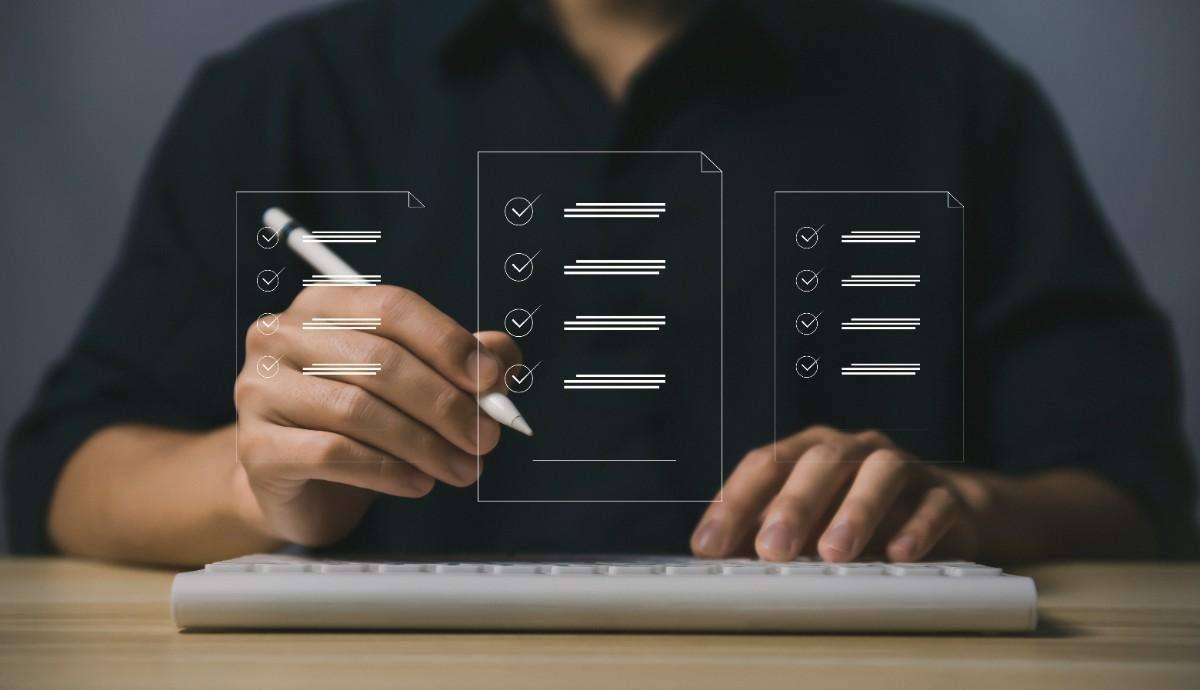

2. Payment Terms
Why It Matters:
Transparent payment terms prevent disputes over compensation and ensure that developers are paid fairly and on time while protecting clients from paying for incomplete or unsatisfactory work.
What to Include:
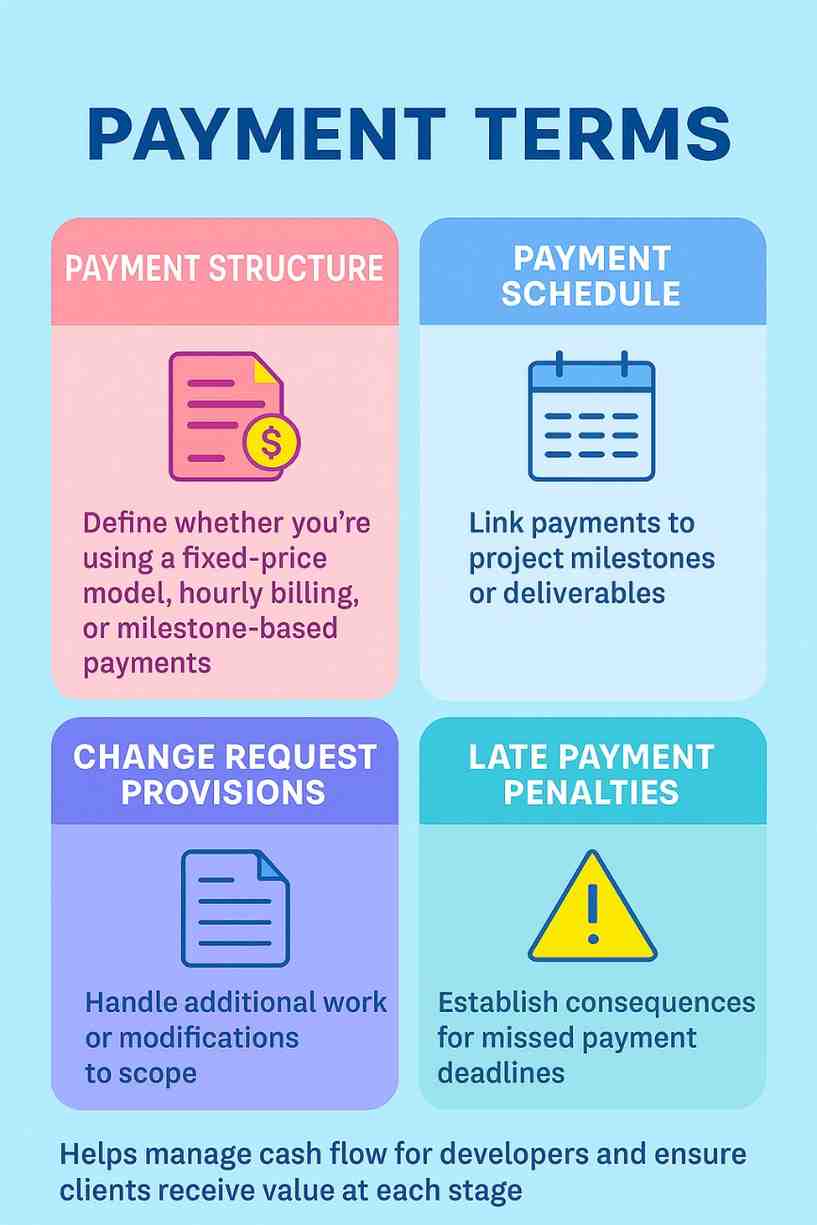
2.1 Payment Structure
Clearly define whether you’re using a fixed-price model, hourly billing, or milestone-based payments. Each approach has its advantages: fixed-price offers predictability, hourly provides flexibility, and milestone-based payments tie compensation to specific deliverables.
2.2 Payment Schedule
Link payments to specific project milestones or deliverables rather than arbitrary dates. This ensures that compensation flows as value is delivered and provides natural checkpoints for project evaluation.
2.3 Change Request Provisions
Include procedures for handling additional work or modifications to the original scope. This should cover how changes are requested, approved, and priced to prevent misunderstandings about additional costs.
2.4 Late Payment Penalties
Establish consequences for missed payment deadlines to encourage timely compensation and provide recourse if payments are delayed.
Clear payment clauses help manage cash flow for developers while ensuring clients receive value for their investment at each stage of the project.
3. Intellectual Property (IP) Ownership
Why It Matters:
Determining who owns your app’s code, design, and other assets is critical for your business’s future. By default, developers may retain ownership of the work they create unless the contract explicitly states otherwise, which could severely limit your ability to modify, sell, or scale your app.
What to Include:
3.1 Explicit Ownership Statement
Clearly state who will own the source code, designs, documentation, and other project assets upon completion. Most clients expect to own these assets, but this must be explicitly stated in the contract.
3.2 IP Transfer Process
Define how intellectual property rights will be transferred from the developer to the client, including any required documentation or formal transfer procedures.
3.3 Third-Party Components
Clarify the use of third-party code, open-source libraries, or pre-existing components. This includes licensing requirements and any restrictions on future use or modification.
3.4 Early Termination Handling
Address what happens to IP rights if the project is terminated before completion, including how partially completed work will be handled.
Failure to address IP ownership can lead to costly legal disputes and may prevent you from making future modifications or selling your app.

4. Confidentiality and Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs)
Why It Matters:
App development often involves sharing sensitive business information, trade secrets, proprietary technology, or innovative ideas that could give competitors an advantage if disclosed.
What to Include:
4.1 Confidential Information Definition
Clearly define what constitutes confidential information, including business plans, technical specifications, user data, financial information, and any proprietary processes or methodologies.
4.2 Protection Obligations
Outline each party’s responsibilities for protecting confidential data, including storage requirements, access limitations, and sharing restrictions.
4.3 Duration of Confidentiality
Specify how long confidentiality obligations will remain in effect, often extending well beyond the contract’s completion to ensure long-term protection.
4.3 Breach Consequences
Define the legal remedies and damages available if confidentiality is breached, providing clear recourse for protecting your business interests.
NDAs are crucial for protecting your app idea and business information from being disclosed or misused, whether intentionally or accidentally.
5. Data Privacy and Legal Compliance
Why It Matters:
Modern apps frequently collect, store, or process user data, making compliance with data privacy laws essential. Non-compliance with regulations like GDPR, CCPA, or local privacy laws can result in substantial fines and serious reputational damage.
What to Include:
5.1 Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Define the legal remedies and damages available if confidentiality is breached, providing clear recourse for protecting your business interests.
NDAs are crucial for protecting your app idea and business information from being disclosed or misused, whether intentionally or accidentally.
5.2 Privacy-by-Design Implementation
Require developers to implement privacy-by-design principles and appropriate security measures to protect user data throughout the development process.
5.3 User Consent Management
Define responsibilities for obtaining proper user consent and managing data subject rights, including the ability to access, modify, or delete personal information.
5.4 Privacy Policy Requirements
Establish requirements for privacy policies and user disclosures within the app, ensuring transparency about data collection and usage.
5.5 Data Breach Procedures
Include protocols for handling data breaches, including notification procedures and remediation steps.
Ensuring legal compliance from the start protects both your business and your users from regulatory action while building trust with your audience.

6. Warranties, Support, and Maintenance
Why It Matters:
Bugs, security vulnerabilities, and technical issues can arise after launch, potentially damaging your app’s reputation and user experience. This clause outlines the developer’s responsibility to address post-launch issues and maintain your app’s functionality.
What to Include:
6.1 Warranty Period
Define a specific period during which the developer will fix defects, bugs, or issues at no additional cost. This typically ranges from 30 days to several months after launch.
6.2 Support Scope and Duration
Clearly outline what types of post-launch support are included, such as bug fixes, security updates, or compatibility updates for new operating system versions.
6.3 Exclusions and Limitations
Specify what types of issues aren’t covered, such as problems caused by third-party service changes, user misuse, or modifications made by other developers.
6.4 Extended Maintenance Terms
Include provisions for ongoing maintenance or updates beyond the warranty period, including pricing and service level agreements.
A well-defined support clause ensures your app remains functional, secure, and competitive after delivery while providing clear expectations for both parties.
7. Dispute Resolution and Termination
Why It Matters:
Even with the best intentions and clearest contracts, disagreements can occur. This clause provides a structured approach to resolving conflicts without resorting to costly and time-consuming litigation.
What to Include:
7.1 Dispute Resolution Procedures
Establish a clear process for handling disagreements, typically starting with direct negotiation, followed by mediation, and finally arbitration or court proceedings if necessary.
7.1 Termination Grounds
Define the specific circumstances under which either party can terminate the contract, such as breach of contract, non-performance, or failure to meet agreed-upon milestones.
7.1 Notice Requirements
Specify the notice periods required for termination and any obligations that must be fulfilled before the contract can be ended.
7.1 Deliverable Handling
Address how partially completed work or deliverables will be handled upon termination, including payment for completed work and transfer of any applicable assets.
Clear dispute resolution mechanisms save time, money, and professional relationships if conflicts arise, while providing a fair process for both parties.

8. Summary of Essential Clauses
Protecting Your Investment
A comprehensive app development contract is essential for safeguarding your interests, clarifying ownership, and ensuring legal compliance. By including these seven essential clauses, you create a solid foundation for a successful partnership and a secure, scalable app launch.
Remember that while this guide provides a strong foundation, every project is unique. Always consult with legal professionals to tailor your agreement to your specific needs, jurisdiction, and industry requirements. As laws and industry standards continue to evolve, particularly around data privacy and digital rights, keeping your contracts current and comprehensive becomes increasingly important for long-term success.
The investment you make in creating a thorough contract will pay dividends throughout your development process and beyond, protecting your business interests while fostering a productive partnership with your development team.

Ready to safeguard your app development project with a rock-solid contract? Book a free 15-minute consultation with a legal-savvy developer who can walk you through essential contract clauses, explain your intellectual property rights, and help you draft an agreement that protects your business from costly disputes. Build your app with confidence—starting with a contract that has your back.